If you plug your laptop’s power adapter into a power socket while the battery is in the laptop, the battery icon on the Windows 10 or Windows 11 taskbar should normally show that it’s charging. But if you see an error message like “0% available (Plugged in, not charging)” when you hover over the battery icon, it likely means that there’s a problem with either the battery driver, physical battery, power adapter, or power cord.
Depending on how bad the issue is, Windows might even show “0% available,” meaning your battery is completely drained. This message indicates that the battery isn’t charging at all, even though you’re sure it’s plugged in correctly or that your laptop has a non-removable battery. This issue is common with Dell, HP, and Lenovo laptops. It can also affect Asus, Acer, MSI notebooks, and Surface or Surface Pro laptops if the battery has been in use for a long time.
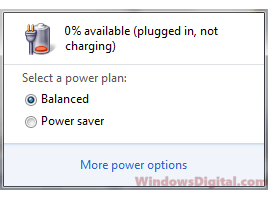
Windows 11 or 10 shows 0% available (Plugged in, not charging)
Sometimes the “Plugged in, not charging” error message can be a false alarm. In some cases, the battery is actually charging, but the Windows battery icon just doesn’t show it. You can confirm if your battery is charging by checking the battery percentage after a few minutes. If it increases, then your battery is charging, and you don’t have to worry about it. However, if the percentage stays the same or even decreases, then you can try the following solutions.
Page Contents
Uninstall the battery driver in Windows 10 or 11
Before we start troubleshooting the hardware, we first have to make sure that the problem isn’t caused by a corrupted or missing battery driver in Windows 10 or Windows 11 for your laptop. In fact, the battery driver is the most common reason users get the “plugged in, not charging” error on their laptops.
To make sure it’s not the battery driver that is corrupted and causing the issue, we have to uninstall the battery driver in Windows 10 or Windows 11. After uninstalling the driver, Windows will then be able to install the correct driver automatically. To do this, follow the steps below:
- In your laptop’s Windows 10 or Windows 11, go to the start menu.
- Search for Device Manager and open it.
- Select and expand Batteries.
- Right-click on Microsoft ACPI-Compliant Control Method Battery.
- Select Uninstall.
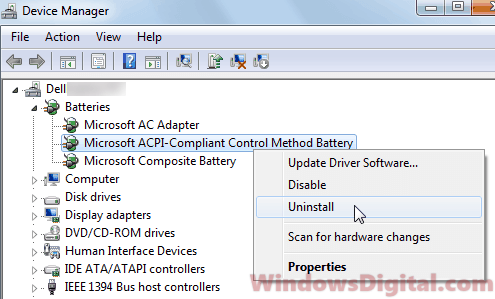
After the uninstall is completed, restart your computer. The next time your laptop boots into Windows, Windows will automatically search for and install the latest battery driver for your laptop. After the reboot, plug in the power cord again and it should show that it is charging now.
If the driver isn’t installed even after several restarts, which is very rare and shouldn’t happen, run Windows Update, and Windows should detect the missing battery driver and install it. On the next reboot, verify if the “plugged in, not charging” message will still show up in Windows 10 or Windows 11.
Check your battery, power adapter, and power sockets
A bad laptop battery, faulty power adapter, or power socket can cause the “plugged in, not charging” error in Windows 10 or Windows 11. Most of the time, it’s the battery that is causing the issue, especially if the battery has already been used extensively for a very long time.
To identify the faulty hardware, troubleshoot your laptop battery using the methods below:
- The very first thing to try is to plug your power cord into a different power socket to make sure it’s not the power socket that is causing the problem. A faulty power socket or a socket with incorrect voltage output may cause your adapter to fail to charge your battery.

- If all different power sockets result in the same error, the next thing to try is to remove the battery from your laptop. (Skip this step if you have a non-removable battery Dell, HP, Lenovo, Asus, Acer, or MSI laptop.) This is to verify if your power adapter is working correctly. If your laptop starts up just fine without the battery inserted, it means that your power adapter is working as it should.
- When the power socket is giving the correct power output and your power adapter is working fine, the only thing left is your battery. Unless you have the same battery model to test with, there is a big chance that the battery is failing. All batteries have a lifespan, and none will work forever. They will eventually fail after a certain amount of repetitive charging. You may want to have it replaced.
What if the problem reoccurs after some days?
If the issue comes right back after a restart, a few days or a few weeks later, it may indicate that something is interfering with the battery driver issue, such as a malware or virus infection.
In any case, at any point in time, you should always have at least one antivirus software active on your PC to protect you from all possible threats. Run a full system scan to check for malware or viruses on your PC. Remove the threats and verify if the problem can be fixed.
If you don’t want to install any antivirus program, at the very least, you should allow Windows Defender to protect your PC. In most laptops such as Dell, HP, Lenovo, Asus, Acer, or MSI, you should have an antivirus software installed. These pre-installed antivirus software usually come as an offer that gives you 30 days free trial.
After this period of time, the antivirus will no longer be active unless you pay for it. If that’s the case, we recommend uninstalling the antivirus software immediately. This is to allow Windows Defender to activate itself when it detects no other antivirus software exists on your computer.