If you want to squeeze every bit of performance out of your AMD Ryzen 5000 or 7000 series processor, you certainly might have heard about Precision Boost Overdrive 2 (PBO2) and its Curve Optimization. These are the things that can help you undervolt and overclock your CPU pretty much automatically while making sure it can run stably. In this tutorial, we’ll show you what PBO2 actually is, why curve optimization matters so much, and how to correctly use them to overclock your Ryzen 7000 or 5000 CPU.
Also see: How to Test CPU Throttling in Windows 11
Page Contents
Supported AMD Ryzen processors with PBO2
Let’s first make sure your processor is one of those that works with PBO2. This feature supports a bunch of popular CPUs from the Ryzen 5000 and 7000 series, like the following.
- Ryzen 5 5600X
- Ryzen 7 5700X
- Ryzen 7 5800X
- Ryzen 7 5800X3D
- Ryzen 9 5900X
- Ryzen 9 5950X
- Ryzen 5 7600X
- Ryzen 7 7700X
- Ryzen 9 7900X
- Ryzen 9 7950X
If you’ve got one of these, you’re set to see what PBO2 can do for you!

Ryzen Master or BIOS, which is better for PBO2?
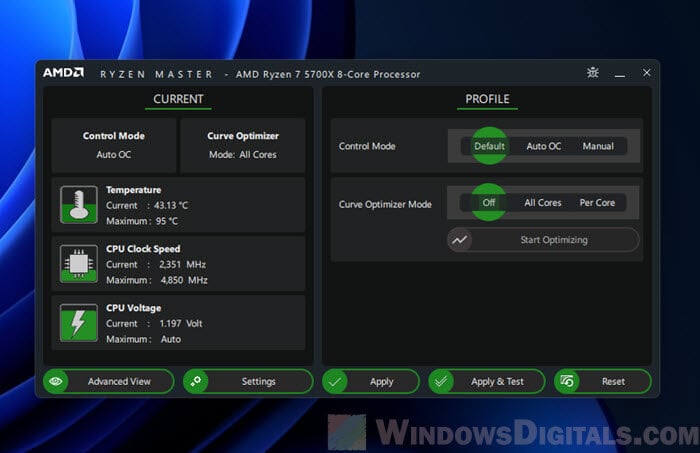
When you’re looking to undervolt and overclock your Ryzen processor, you have two main tools: Ryzen Master and the BIOS. Each has its perks and caters to different user preferences.
Ryzen Master:
- It provides an easy-to-use interface which is pretty good for beginners.
- You can tweak settings on the go without needing to reboot your system for every changes you make (though some changes might still require a reboot).
- It lets you save different profiles for different activities, like gaming or work (e.g. you might not want to OC too much for work).
BIOS:
- The BIOS gives you deeper customization options, some of which might not be available in Ryzen Master.
- Changes in the BIOS are generally more stable as they are applied system-wide.
- You don’t need to install any extra software since the BIOS is part of your motherboard.
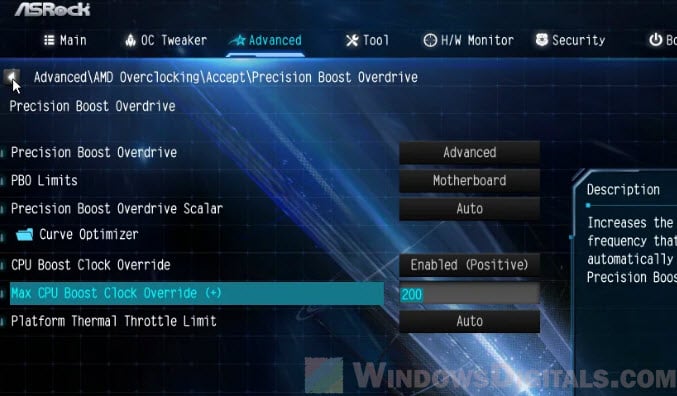
We’ll be using Ryzen Master in this guide because it’s easier for most people. However, if you prefer getting hands-on with the BIOS and are comfortable with it, go ahead and use it for your tuning.
Linked issue: Ryzen Master unable to initialize Kindly reinstall the program
What are PBO2, Curve Optimization, and Boost Override?
Precision Boost Overdrive 2 (PBO2) is an advanced overclocking feature from AMD for Ryzen processors that lets you push your CPU beyond its normal limits while keeping everything stable.
- With Curve Optimization, you can fine-tune the voltage curve, lowering the voltage at higher frequencies.
- Boost Override CPU (Auto OC) lets you raise the maximum boost clock, which could mean better performance in tasks that don’t use many cores.
- Power Limits (PPT, TDC, EDC) let you manage the power going to your CPU.
Next, we’ll look at how to use these features to overclock your Ryzen 5000 or 7000 series processor.
First step: Find the best curve using Curve Optimizer
The first thing to do is find the best curve with the Curve Optimizer in Ryzen Master. This helps you undervolt your CPU, which cuts down on power use and heat, but without losing performance.
- Start Ryzen Master on your computer.
- Switch to Advanced View in Ryzen Master for more detailed settings.
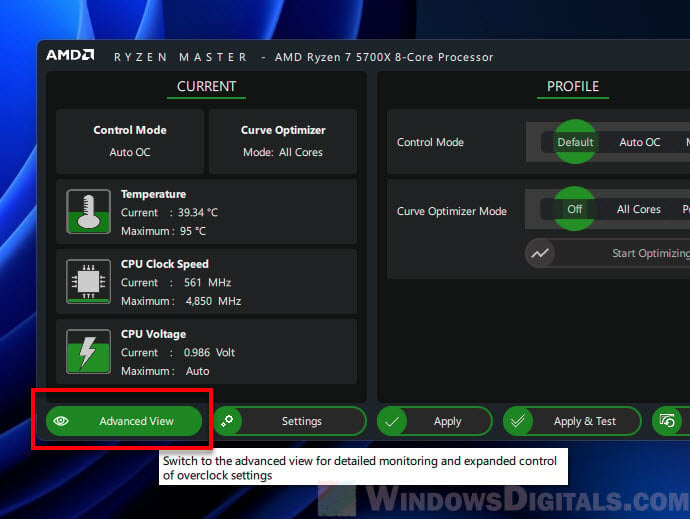
- Pick Curve Optimizer from the menu on the left.
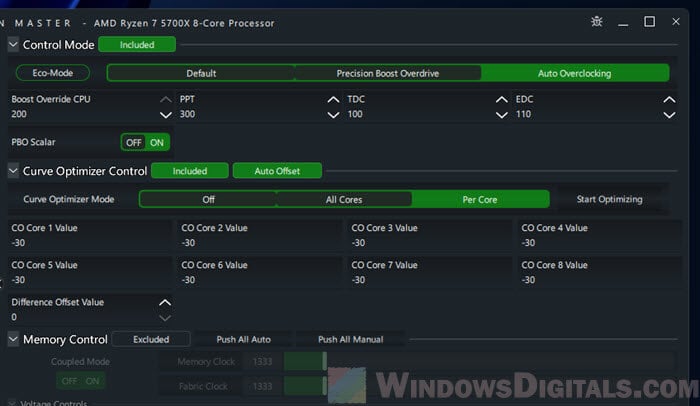
- In Control Mode, choose Auto Overclocking.
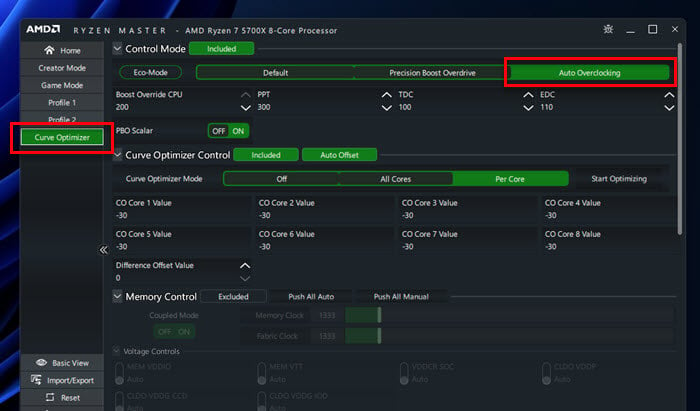
- Before you adjust the curve, set the PPT (Package Power Tracking), TDC (Thermal Design Current), and EDC (Electrical Design Current) to the default values for your processor. Look these up online for your specific Ryzen model. For instance, default values for a Ryzen 5700X are PPT: 76W, TDC: 60A, and EDC: 90A, and for a Ryzen 5800X, PPT: 142W, TDC: 95A, and EDC: 140A.
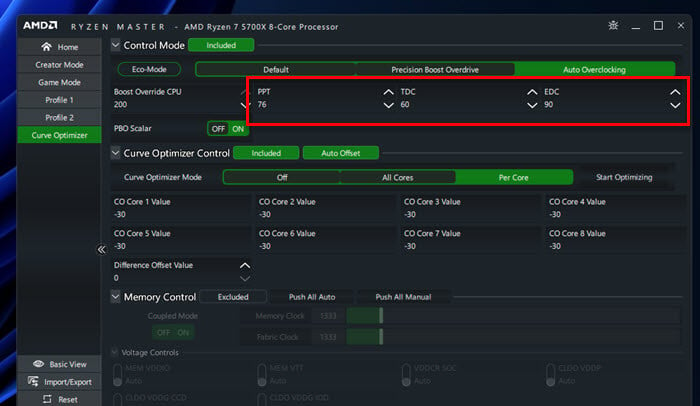
- Keep the Boost Override CPU setting as it is for now.
- For the Curve Optimizer Control, choose Per Core mode. This lets you adjust each core separately for better results.
- Click Start Optimizing to begin the process. Ryzen Master will try different settings to find the best one for your processor.
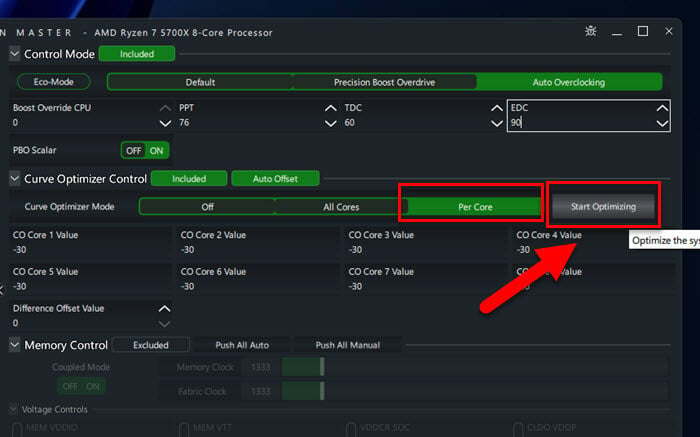
- When Ryzen Master found the best curve, click Save Profile and then Apply to keep your settings.
Common problem: PC Keeps Restarting When Opening Ryzen Master
Note that -30 is the max for the Curve Optimizer. If Ryzen Master hits -30 for your cores, you’ve got a golden chip.
Why use “Per Core” mode instead of “All Cores”?
It’s about precision. Each core may behave a bit differently and have varying limits. Thus, tuning them one by one can let you find out the max you can go for each core, instead of using the max of the weakest core for all cores.
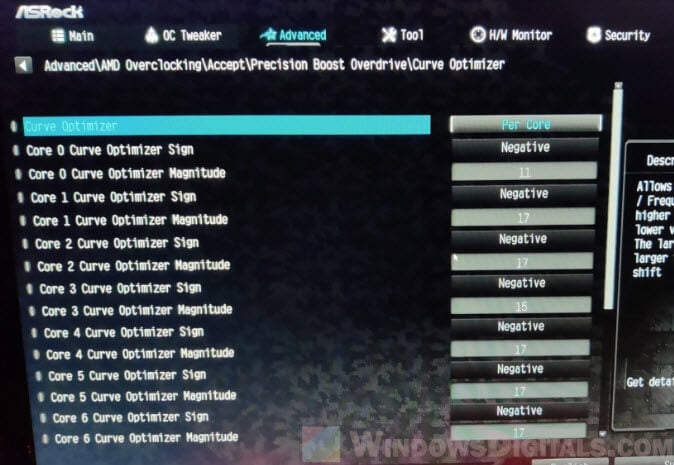
BIOS manual curve optimization (optional for pros)
For those who know their way around, the BIOS is sometimes a better place for manual tuning. Start with a negative curve, like -5, on all cores and check how stable it is with apps like Prime95 or Cinebench. Slowly increase the negative value, testing stability each time, until you find the best setting or your system starts having issues.
Second step: Find the maximum “Boost Clock Override”
After tuning your CPU’s voltage curve, the next thing to do is to find the highest Boost Clock Override your processor can actually handle without crashing.
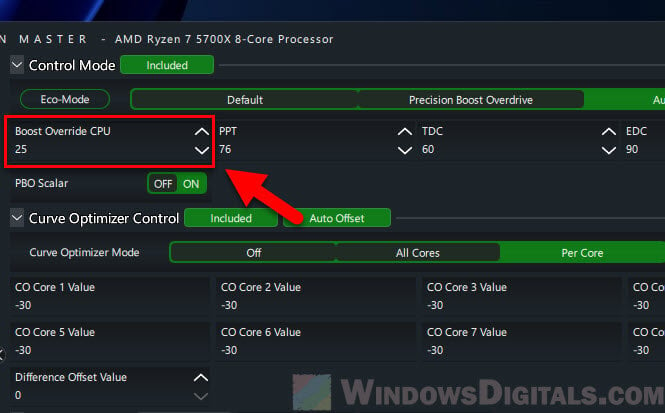
- In the Curve Optimizer in Ryzen Master, start by raising the “Boost Override CPU” by 25 MHz. Click “Apply” to save the changes.
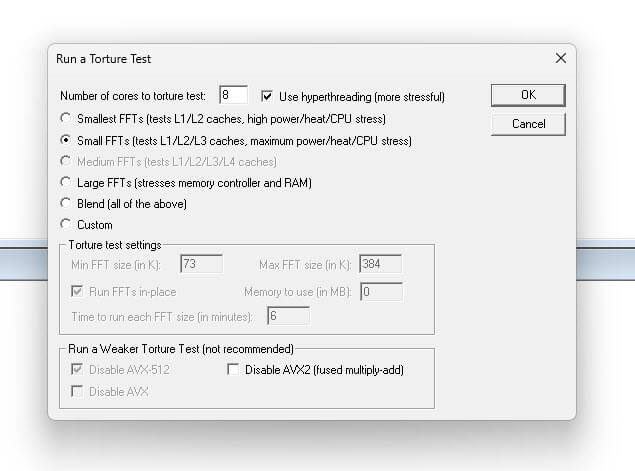
- You’ll need to restart your computer to apply these changes. Once restarted, use tools like Prime95, OCCT, or Cinebench to test your CPU’s stability. You could, for example, run Prime95 (Small FFTs) for 10 minutes to see how it holds up.
- If there are no issues, go back to Ryzen Master and up the Boost Override CPU by another 25 MHz. Save the changes, restart, and test again.
- Keep doing this, raising the boost by 25 MHz at a time and testing each setting. Eventually, you’ll reach a point where your system isn’t stable anymore. When that happens, just go back to the last stable boost value you found. This will be the best setting for your CPU.
- Some processors, known as “golden samples,” can handle up to a 200 MHz boost without problems. But this isn’t really common, and it’s all about luck when you buy your CPU.
Suggested read: Why is my CPU Overheating and How to Fix it?
Third step: Find the most suitable power limits
Now that you’ve optimized your CPU’s curve and found the best Boost Clock Override, you’ll now need to find the most suitable power limits. This includes the Package Power Tracking (PPT), Thermal Design Current (TDC), and Electrical Design Current (EDC).
- These are the technical terms you need to know about setting the power limits:
- PPT (Package Power Tracking) is the max power your CPU can draw. A higher PPT means your CPU can keep up its performance longer. But setting a PPT doesn’t mean your system will always use the max wattage; it only uses what it needs and is allowed to.
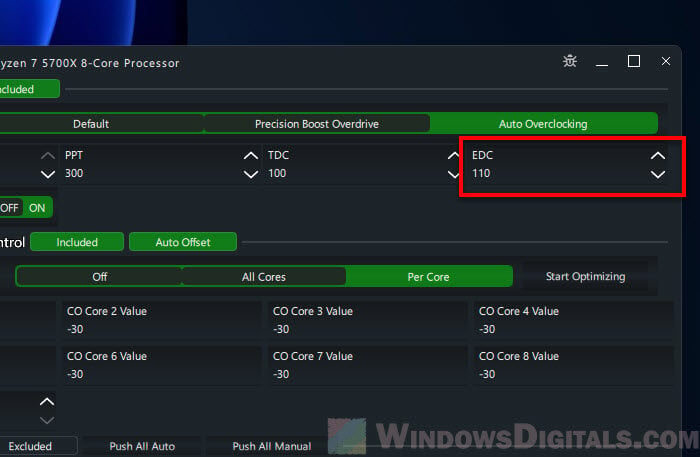
- TDC (Thermal Design Current) is the max current your CPU can handle under thermal limits.
- EDC (Electrical Design Current) is the max current for quick and intense tasks.
- Start by setting the PPT to a level that fits your needs. If power use isn’t a big concern for you, feel free to set it high. Ryzen Master sometimes defaults to 500 or 1000. Just remember, setting a high PPT doesn’t mean your system will always use that much power; it only uses what it needs. If you have a specific wattage in mind, set the PPT to that.
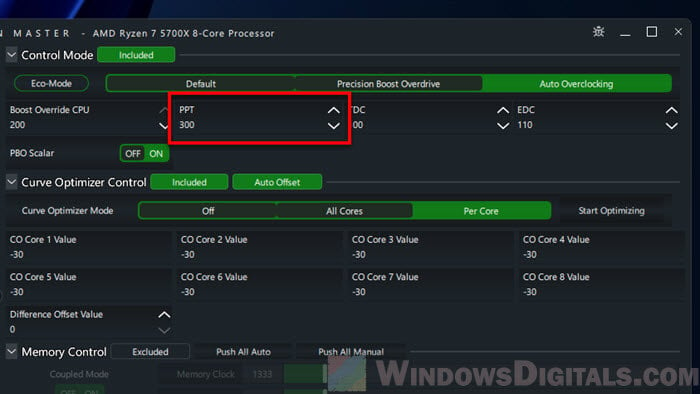
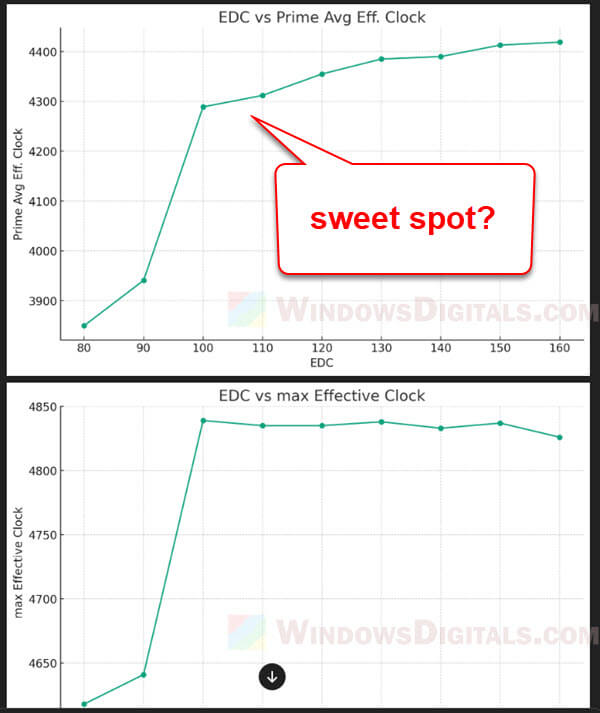
- Next, tuning the EDC (the most impactful power limit).
- Increase the EDC value step by step, starting with a +10 boost.
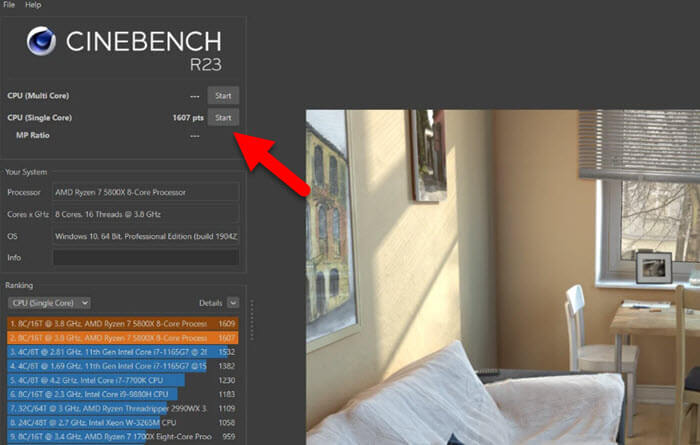
- After each adjustment, run a benchmark like Cinebench and record the “Single Core” and “Multi Core” scores.
- Also, track your CPU’s average effective clock speed and temperature during the test with a tool like HWiNFO64.
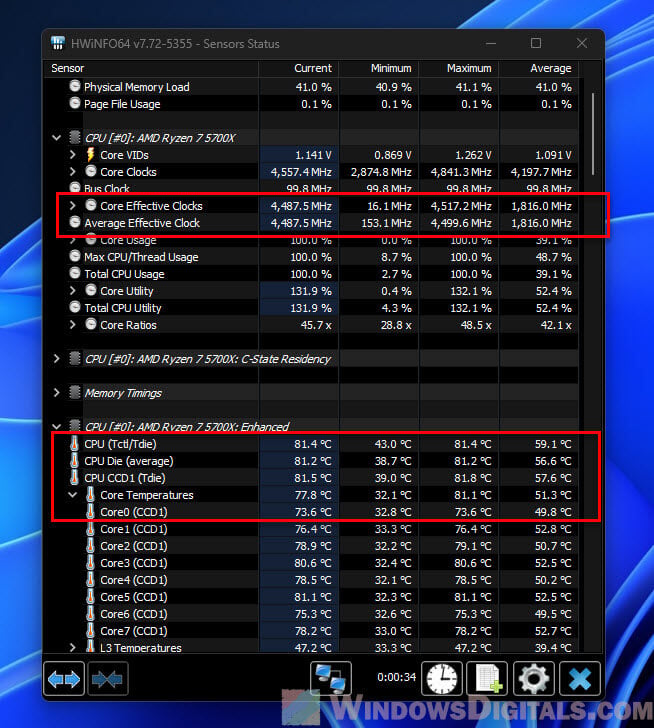
- Keep a record of your results, maybe in a spreadsheet, and consider making a graph to see how different EDC values affect performance.
- Increase the EDC value step by step, starting with a +10 boost.
- Then, find the EDC value that gives the best mix of performance and temperature for what you need. Higher EDC values don’t always mean better performance, and lower ones aren’t always worse.
- Finally, adjust the TDC. TDC usually affects performance less than EDC. You can set it a bit lower than the EDC value or leave it higher and let the system manage it.
And that’s all there is to it. With the curve optimized, the Boost Clock Override set, and the power limits tuned correctly, your CPU should be running at its peak.
Read next: How to Disable CPU Throttling (Settings) in Windows 11
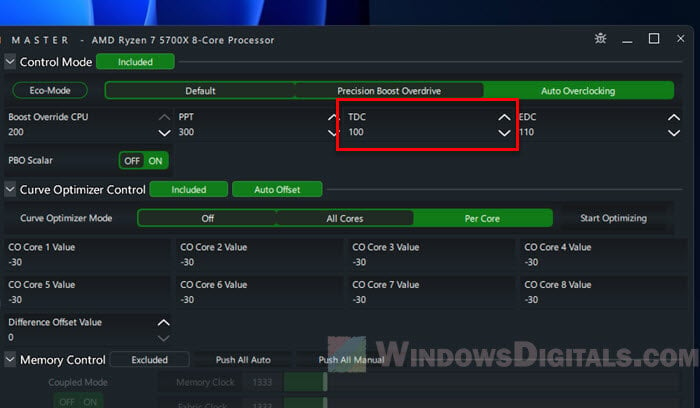
The screenshot below shows the settings for my golden sample Ryzen 7 5700X, which follows exactly the same order of tuning listed in this guide – Curve Optimization first, Boost Override next, then power limits last. It is still running stable to this date.