A ghost file is a file that is still visible in File Explorer but Windows returns “Item not found” or “File not found” error when you try to delete it. It is there but at the same time not actually there. This guide shows a few solutions on how to get rid of a ghost file or folder in Windows 11 or Windows 10.
Page Contents
Delete a Ghost File in Windows 11/10
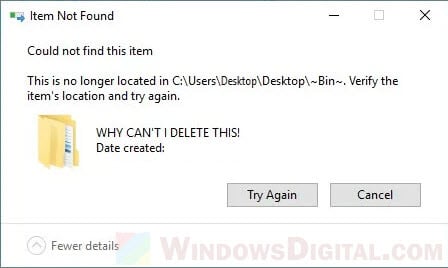
Error that may be prompted to you when you try to delete a problem ghost file in Windows 11/10 – “Item not found – This is no longer located in this directory. Verify the item’s location and try again” . It could also happen when you try to delete a folder where there is nothing in it.
To delete a ghost file in Windows 11 or Windows 10, try one of the following solutions below.
The solutions below are also applicable to the error “File access denied – You need permission to perform this action” when you delete a file or folder.
Fix 1 – Restart PC and try again
The “Item not found” issue is often due to an error with file explorer that appears to still display a file despite it being deleted already and no longer exist in the current Windows session. In many cases, the ghost file will simply disappear on next restart.
Try to restart your PC and see if the file still exists. If it’s still there, try to delete the ghost file or folder again.
Fix 2 – Delete ghost file in safe mode
Try to delete the ghost file or folder in safe mode. Entering safe mode is to ensure that the file would not be in used or locked by any software or program.
To enter safe mode, go to Windows Start menu, click on Power. Then, while holding Shift key, click on the Restart button.
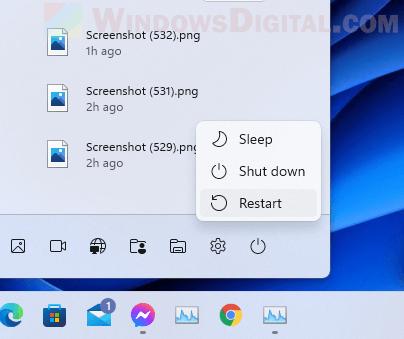
Windows 11
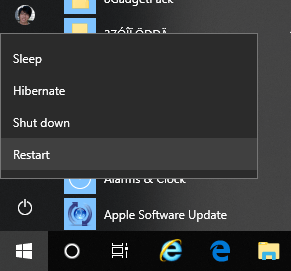
Windows 10
When the startup settings shows up, press the 4 key to enable safe mode on your next startup.
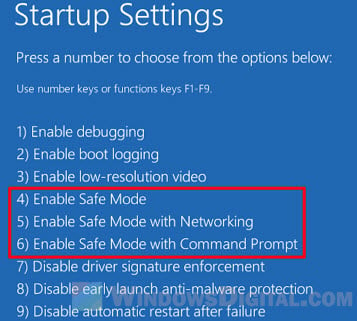
Once you’re in safe mode, try to delete the ghost file or folder again.
Fix 3 – Use RD command in an elevated command prompt
The rd command is used to remove an empty directory, and optionally, to delete a directory and all contents in it. An elevated command prompt is a command prompt session with administrative privileges. In order to execute the rd command, you need to first run command prompt as administrator.
- On Windows 11/10 search bar, search for “cmd” or “command prompt“.
- Right-click Command Prompt and then select Run as administrator.
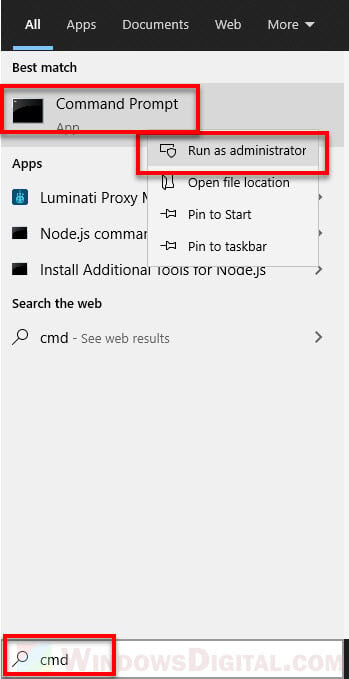
- In the command prompt window, enter the following command.
rd /s "PathToTheFolder"
For example:
rd /s C:\CantDeleteThis
The /s parameter is to tell the command to delete all files and sub-folders in the directory.
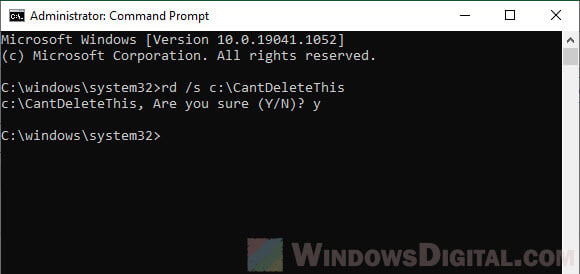
- The ghost folder should now be deleted.
Fix 4 – Use a deletion software such as Unlocker
There are many file deletion software that are able to force delete an undeletable file or folder in Windows. We recommend Unlocker by IObit. It is one of the most popular tools well known for its ability to unlock a locked file or folder that may be in used by a program or software so that it can be deleted, moved or renamed.
You can download Unlocker from https://www.iobit.com/en/iobit-unlocker.php. Once downloaded, install it.
To unlock and delete a file or folder, right-click on the ghost file or folder. Then, select IObit Unlocker from the context menu.
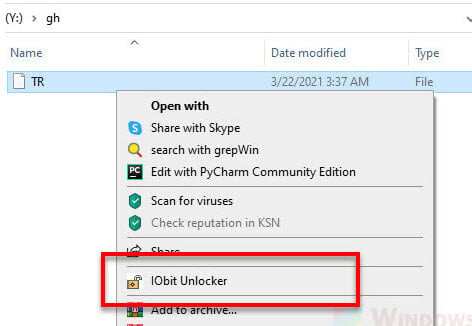
In the Unlocker pop up window, enable “Forced Mode” and then click on Unlock to unlock the file. Once unlocked, try to delete the ghost file or folder again.
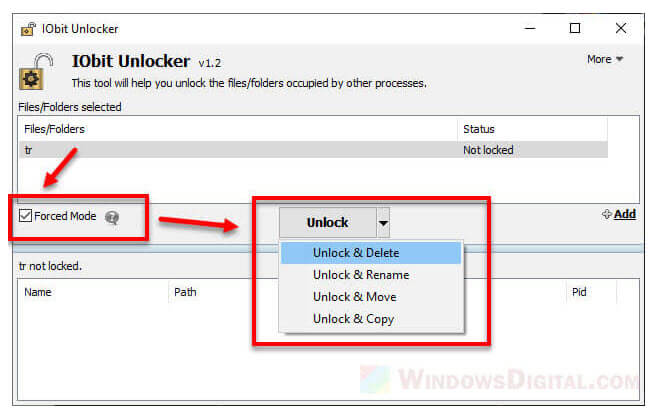
Optionally, you can click on the drop down button next to the Unlock button to expand other available options. Select Unlock & Delete if you want Unlocker to also delete the file for you.