When you buy a 240Hz monitor and feel excited because you’re expecting to see a very smooth 240 frames per second refresh rate, but it turns out it can run only at 144Hz, know that there are several things that can cause this problem. This can happen regardless of your OS version, be it Windows 11 or Windows 10. This guide will look into why this happens and how to fix it.
Also see: How to Change Desktop Screen Refresh Rate in Windows 11
Page Contents
Check if your ports can handle the high refresh rate
Check the ports on your computer. To run a 240Hz monitor at 1440p, you need a lot of bandwidth (about 26.54 Gbps). Not all ports can handle this. For example, HDMI 2.0b often can’t meet these high demands.
If your laptop or desktop’s ports don’t support enough bandwidth, your monitor won’t show its maximum refresh rate. This isn’t just about the ports on your computer but also about what your monitor can handle. For example, if you only have HDMI 2.0b but your monitor needs something better for 240Hz, you’ll actually be stuck with a lower refresh rate.
Similar problem: 144Hz Monitor Only Showing 60Hz in Windows 11, Why?
Cables actually matter a lot
The type and quality of your cable are key to how well your monitor works. If you’re trying to get 240Hz at 1440p, HDMI 2.0b won’t cut it because it can only handle up to 18 Gbps. DisplayPort 1.4 is much better as it goes up to 32.4 Gbps.
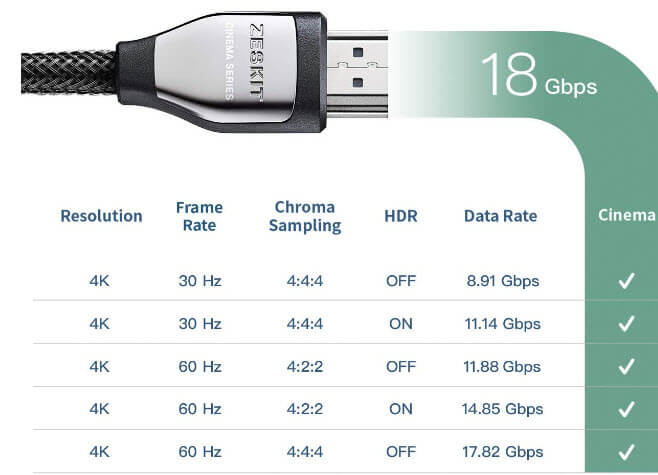
If you’re using an old HDMI cable or a cheap DisplayPort cable, your monitor might not go past 144Hz or even 60Hz. To get 1440p at 240Hz, you need a cable that can handle the high bandwidth needed for that performance.
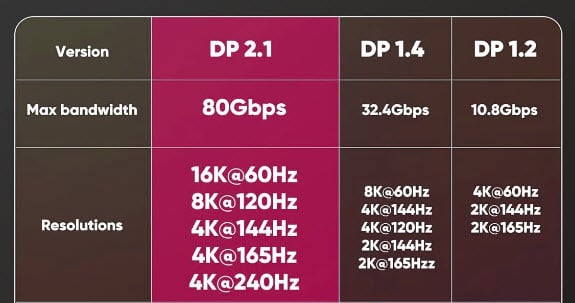
- DisplayPort 1.4: This is usually the best choice for 1440p at 240Hz. It can handle up to 32.4 Gbps and uses Display Stream Compression (DSC) to keep high resolution and refresh rates without losing quality.

- DisplayPort 2.0: It’s not as common but still good. It supports up to 80 Gbps and works even better for higher resolutions and refresh rates.
- DisplayPort 2.1: This is a newer option that handles more than three times the bandwidth of DisplayPort 1.4, which means it’s great for 1440p at 240Hz and even higher settings. Note that devices with DisplayPort 2.1 and 2.0 are still quite new in the market.
- HDMI 2.1: This is another good option, especially with a bandwidth of 48 Gbps, perfect for 1440p at 240Hz. But, both your monitor and graphics card need to be HDMI 2.1 compatible.
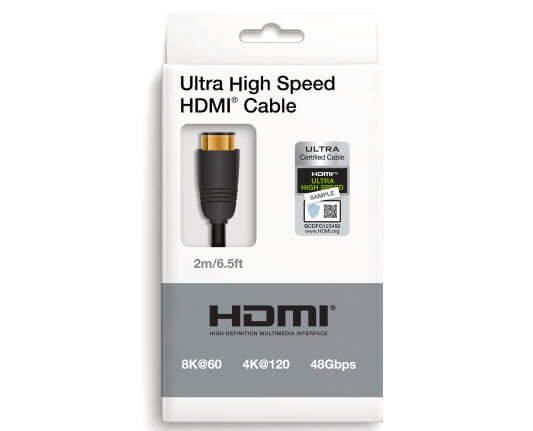

Make sure to buy a high-quality cable from a trusted brand. Cheaper cables might not deliver what they promise.
It’s also good to know that not all devices support the new standards like DisplayPort 2.0 and HDMI 2.1 yet.
After getting a better cable, check your monitor’s settings to make sure it’s set to run at 240Hz.
Related resource: Mouse Lag on 4k Monitor or TV Screen (Fix)
Update your graphics driver
In most cases, if the graphics driver is outdated or incorrectly installed, it can cause problems such as monitors showing only 144Hz when it’s supposed to be 240hz.
Sometimes, your Nvidia Control Panel might not work with your current drivers. This problem can stop you from changing the refresh rate. To fix this, make sure your graphics drivers are updated. Nvidia often updates its drivers to support new tech and fix bugs. You can get the latest drivers from Nvidia’s website.
Also, install the Nvidia Control Panel with your drivers to tweak different display settings, including the refresh rate. If you run into problems with the Nvidia Control Panel, like error messages about driver compatibility, it’s best to install the latest drivers from Nvidia’s website instead.
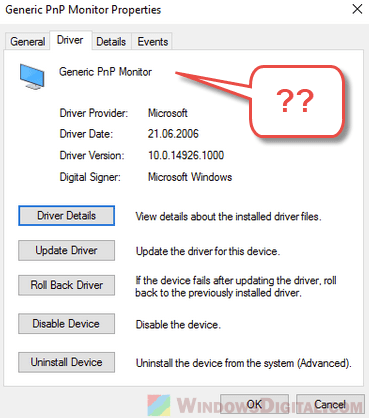
Another thing to check is how your operating system sees your monitor. Sometimes, it’s seen as a “Generic PnP Monitor” in the Device Manager, which might limit what you can do, including the refresh rate. To fix this, update your monitor driver or pick the right monitor model in your system settings. This is important to make sure your system fully uses your monitor’s capabilities and lets it run at the highest refresh rate.
Check your monitor’s ability and settings
Sometimes, the problem isn’t with your computer or cables but with the monitor itself. Make sure your monitor can actually run at 240Hz. Although this seems simple, there’s often confusion about monitor specs.
First, look at your monitor’s manual or specs online to make sure it supports 240Hz at your current resolution. Some monitors only do 240Hz at lower resolutions.

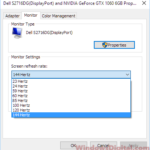
If your monitor can run at 240Hz, you can change the refresh rate by going to “Display Settings“, then “Advanced Display Settings“, and then “Monitor Properties“. Here, you can pick the refresh rate you want if it’s available.
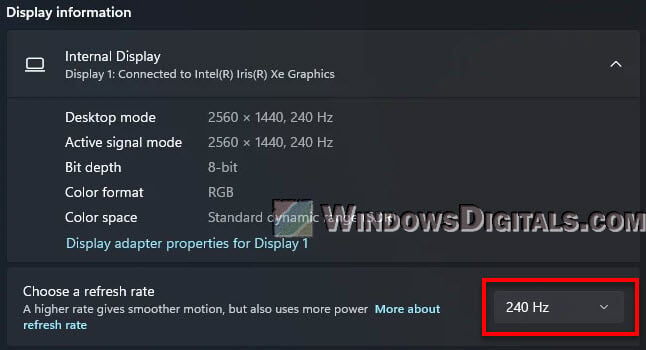
If you can’t find the right refresh rate, try creating a custom resolution in the Nvidia Control Panel (for Nvidia GPU users). This lets you set the resolution and refresh rate yourself.
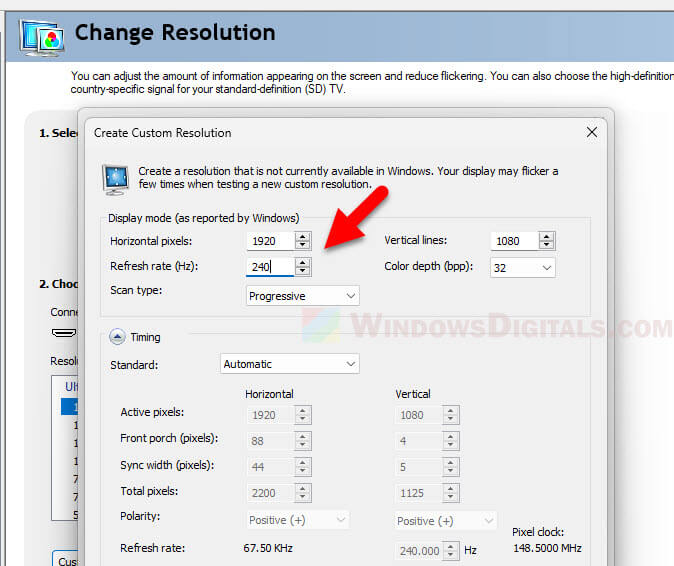
Also, some monitors have specific needs or limits based on their design. For example, some G-Sync monitors can only reach certain refresh rates over HDMI.
Pro tip: 16:10 vs 16:9 Aspect Ratio for Gaming: Which is Better?
How using two monitors can affect refresh rates
If you are using multiple monitors for your PC, it is a common problem where often you can’t get the 240Hz monitor to run at 240Hz. The problem is often caused by how the graphics outputs are set up on your computer, especially in laptops.
![]()
Some users unintentionally connected the high refresh rate monitor to the integrated GPU instead of the dedicated GPU on their laptops. This, as a result, will cause problem like the monitor running with limited refresh rate (e.g. 144Hz when it can run 240Hz). That is because integrated GPUs are generally weaker than dedicated GPUs like those by NVIDIA and AMD.
In many laptops, the ports that can support high refresh rates are connected to the integrated GPU on the motherboard instead of the dedicated GPU. This setup can cause issues where, even though you have a powerful dedicated GPU, the laptop uses the weaker integrated GPU’s capabilities when an external monitor is connected. For example, the integrated Intel GPU might only support up to 144Hz at 1440p, even if the dedicated GPU can do more.
Linked issue: Second Monitor Keeps Flashing or Going Black Randomly
Fixing this can be complicated and sometimes impossible. One thing you can try is to check if there are any settings in the BIOS that let you change which GPU the external outputs are linked to. But this option isn’t usually available in most laptops.
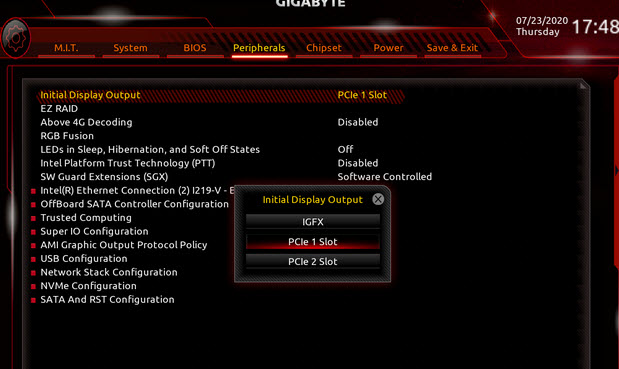
Another idea is to use specific types of docking stations or external GPU boxes that connect via Thunderbolt 3 or other high-bandwidth connections. These might help get around the limits of your laptop’s GPU outputs. But they can be quite pricey and don’t always work.

Also, even if your laptop’s hardware supports 240Hz, the software or drivers might limit it based on how you’ve set up your dual monitors. Sometimes, updating drivers or changing software settings can fix these issues, but not always.