Like most other components in a computer, CPU is designed with heat dispersion and ventilation in mind so they don’t accumulate too much heat as you use it. If any of the components in the cooling system fails or becomes too old to continue functioning, it will cause the CPU to overheat.
CPU overheating does not usually happen, but when it does, it could cause serious issues such as sudden and frequent blue screen, random restarts, or even causing damage to the component. In this write-up, we will show you the symptoms of CPU overheating, how to tell if your CPU is overheating, why does your CPU keep overheating and how to fix it.
Also see: How to Limit CPU Usage of a Process in Windows 11

Page Contents
CPU overheating symptoms
Below are a few of the most common symptoms you may encounter when your CPU is overheating.
- CPU throttling – You may experience a sudden slow down or lag when you use an app or play a game.
- Blue screen of death (BSOD) – Windows 11/10 crashing, unstable and forced shut down.
- Random and repetitive restart – Computer randomly restarts without prior warning and may be repetitive.
- CPU Fans (if it’s an air cooling system) are running intensively and making very loud noises.
Modern CPU has a protection feature which will force shut down the CPU when it detects the temperature gets to an critically dangerous level to prevent damage to the hardware. This is why you may encounter frequent and random shutdown/restart when your CPU is overheating.
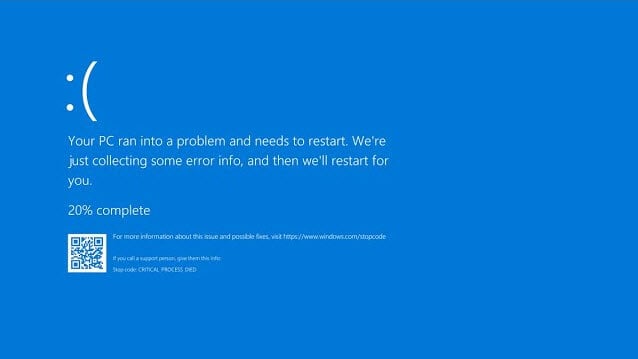
How to check CPU temperature
There are a couple of ways to check your CPU temperature. You can check your CPU temp by either going into the BIOS or by using a third party hardware temperature monitor tool. The most recommended way to check your CPU temperature accurately is to use a tool called Core Temp.
https://www.alcpu.com/CoreTemp/
Once you have installed Core Temp, open it to see the temperate of each of your CPU core.
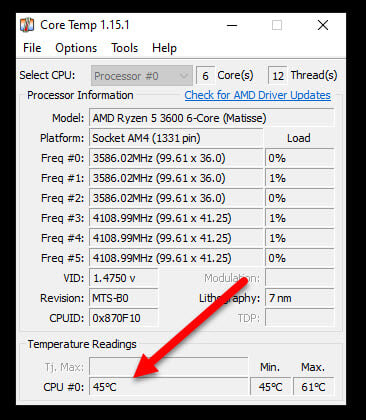
How hot is too hot for the CPU?
This question greatly depends on the brand, generation and model of the CPU – whether it’s an Intel or AMD CPU, i9, i7 or Ryzen generation, etc. Each CPU has its own average range of ideal and maximum temperature. Some CPU can withstand much more heat than the others. You should read the manual (or check online) for info regarding to the acceptable temperature range of your CPU.
Generally, you can refer to the table below to get an idea of when you should be concerned about your CPU overheating.
| Below 60 Celsius | You’re good. |
| 60-70 Celsius |
Normal when you are running an app or a game. |
| 70-80 Celsius |
Acceptable when you are running intense app or game. |
| 80-90 Celsius | Not good. |
| Above 90 Celsius |
Warning! |
You should also be concerned if your CPU goes above 70 Celsius when it is completely idle. The idle CPU temperature also depends on the temperature of the surrounding environment (e.g. the temperature of your room). For example, you may see a few degrees higher idle CPU temperature during the summer.
Related: How to Set Process CPU Affinity or Priority Permanently in Windows 11
How to fix CPU overheating
Below are 5 tips on how to stop and prevent CPU overheating on a desktop or laptop computer.
Fix 1: Disable overclocking
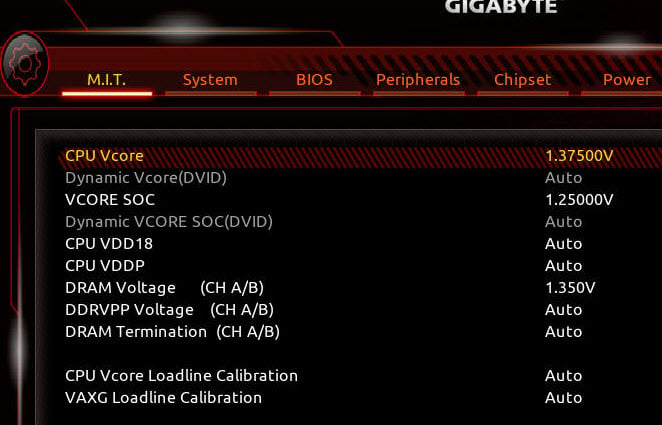
Other than the cooling system or the hardware being the reason for CPU overheating, another common cause for CPU overheating is overclocking. Overclock is a technical term used to describe a situation when a hardware part such as the CPU is set to run beyond what it is capable of.
When overclocking a CPU, you have to increase the CPU’s voltage so that it can maintain its increased clock speed. As you increase the voltage, the CPU gets hotter. If the cooling system cannot cope with the excessive heat, your CPU may overheat.
If you did overclock your CPU, try to tune down the overclock settings or disable the overclock and see if the CPU overheating issue is resolved. Should you want to continue overclocking your CPU, you may want to consider upgrading your CPU cooling system (e.g. liquid cooling).
If you have no idea if you are running any overclock setting and you notice your CPU overheating on startup or when you play a game, check your computer to see if there is any overclock related software running in the background which you may not know of. Here are some of the most common overclocking software: MSI Afterburner, Intel Extreme Tuning Utility, AMD Ryzen Master, NVIDIA Inspector, CPU Tweaker, EVGA Precision X, ASUS GPU Tweak.
If you find any of these software currently running in Windows 11/10, try to remove any applied overclock settings, disable the overclock or revert the CPU clock speed back to its default.
Since CPU overclocking is usually applied via the BIOS settings, you should also check your computer’s BIOS settings to see if there is any applied overclock settings. Try to disable any overclock settings in the BIOS or revert the CPU clock speed settings back to its default.
Fix 2: Clean the inside of your computer
Dust will build up in your computer case as time passes. At some point, your case and all the fans in it are going to get so dusty that it may deteriorate the ventilation in the case and cause heat to trap inside. Dust is the most common cause for most computer overheating issues as it blocks airflow.
To reduce the heat trap and allow smoother heat dispersion and ventilation in your computer case, clean the dust collected around the CPU fan, heat sink and other parts in your computer case.

To prevent CPU overheating in the future, you should clean your computer case and the fans regularly – once every few months depending on the surroundings where you place your computer case.
Fix 3: Check the CPU fan
All computer fans have a life span (e.g. around 30,000 hours). Normally when a fan is failing, the first sign may be the strange noise that comes from it. When a fan starts to fail, it spins slower and slower until it is no longer effective for heat dispersion.
Check the CPU fan (and other fans in the computer case as well) to make sure it is properly plugged and is operating at its maximum efficiency. Make sure to also regularly clean the dust that clogged up the fan to ensure its effectiveness.

If you are using a liquid cooling system for your CPU, check the pump and make sure it is functioning properly and efficiently.
Fix 4: Check the thermal paste of your processor
Thermal paste is a thermally conductive chemical substance used between the CPU and the heat sink. Its role is to eliminate air gaps and spaces between the processor and heat sink so that heat transfer can be at its maximum efficiency.
Thermal paste can significantly affect the temperature of the processor. It is generally not okay to run a CPU without thermal paste as it will certainly overheat because of the air gaps trapped between the processor and the heat sink, which will significantly reduce the heat transfer efficiency.
Thermal paste can also deteriorate over time. It will gradually lose its efficiency as time passes. How long the thermal paste can last depends greatly on the quality of the thermal paste.
Most thermal paste can generally last a good couple of years, after which you will have to wipe the old thermal paste off the CPU (with rubbing alcohol), and then apply a new thermal paste. You should check out some videos on YouTube about how to do this before doing this yourself for the first time, or let the professionals do it for you.

Fix 5: Make sure there is enough airflow in the computer case
Most computer cases are designed with multiple fans in particular places to create sufficient air flow to remove heat produced by all the parts of your computer (e.g. CPU and GPU). Make sure all these fans are working properly and don’t have too much dust caught in them.
Also, make sure there is enough room in the computer case for air flow. Too many hardware parts, such as excessive number of internal hard disk drives, can block air flow and trap heat in the casing, which will ultimately increase the temperature of all the hardware parts (such as CPU) in the computer case.
Additionally, make sure you leave enough space around the computer case so that fresh air can get in and hot air gets out of the computer case easily. If you are using a laptop, a laptop cooler – a raised platform (usually with fans) for you to place your laptop on, may help reduce the overall temperature of your laptop.